The Future of Cybersecurity: Navigating NIST CSF 2.0 with IRM
In the complex and ever-changing cybersecurity landscape, the newly released NIST Cybersecurity Framework (CSF) 2.0 emerges as a beacon for organizations striving to manage and mitigate cybersecurity risk. Integrated Risk Management (IRM) technology plays a pivotal role in this journey, bridging the gaps between various risk management disciplines and fully integrating cybersecurity risk with Enterprise Risk Management (ERM). This post delves into the intricacies of the NIST CSF 2.0 and explores how IRM technology serves as a catalyst for comprehensive risk management.
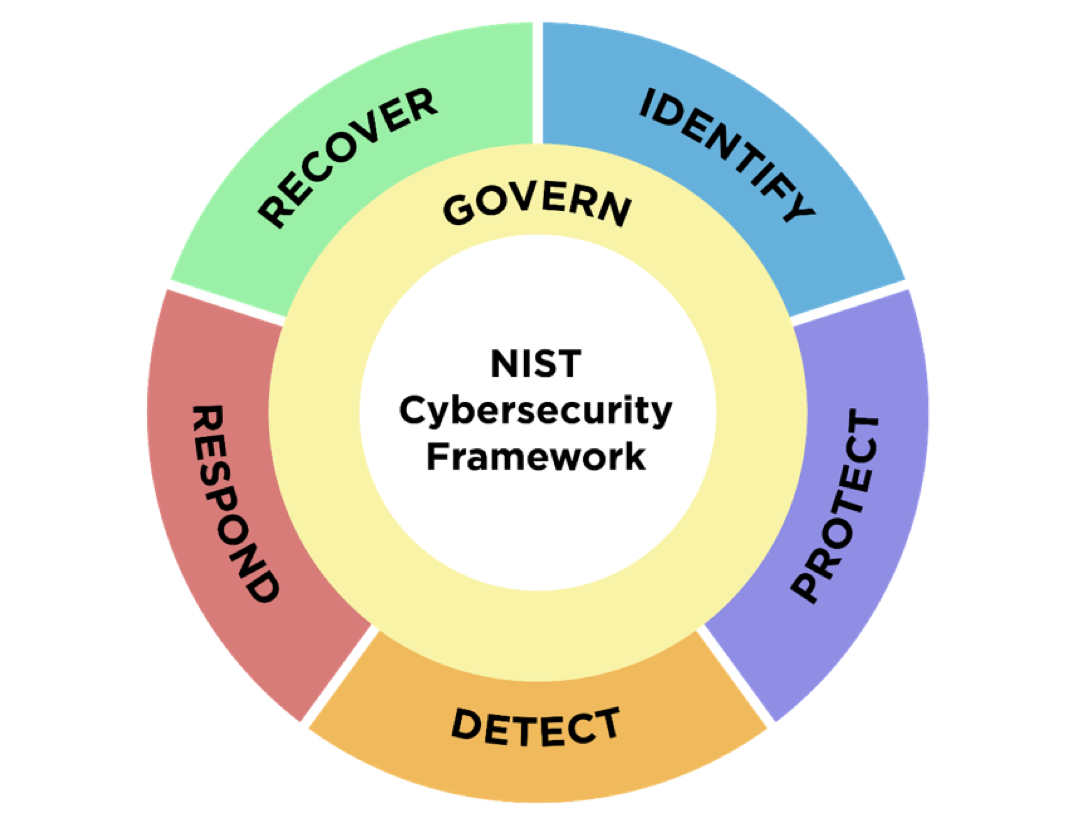
The NIST Cybersecurity Framework (CSF) 2.0: A Comprehensive Overview
Source: National Institute of Standards and Technology
The NIST CSF 2.0 is not just a set of guidelines; it's a strategic compass for organizations to manage and mitigate cybersecurity risk. It emphasizes the importance of integrating cybersecurity risk management with ERM, ensuring that cybersecurity efforts are not in silos but are integrated into the broader organizational strategy.
Understanding the Framework
The NIST CSF 2.0 consists of several key components that guide organizations in managing cybersecurity risks:
Functions: Govern, Identify, Protect, Detect, Respond, and Recover. These functions provide a high-level view of an organization's cybersecurity risk management.
Categories and Subcategories: These break down the functions into specific outcomes for technical and/or management activities.
Informative References: These are specific sections of standards, guidelines, and practices that illustrate a method to achieve the outcomes associated with each subcategory.
The Importance of Integration
The NIST CSF 2.0 emphasizes the integration of cybersecurity risk management with ERM. This alignment ensures that cybersecurity is not an isolated function but is integrated into the broader organizational strategy. By aligning cybersecurity efforts with overall business goals, organizations can ensure that they are not just secure but are also poised to leverage the myriad opportunities that the digital age offers.
Risk Integration in NIST CSF 2.0: The Role of Integrated Risk Management (IRM)
IRM technology enables risk integration as defined by the NIST CSF 2.0. Here's how:
Aligning Cybersecurity and Privacy Frameworks: IRM integrates cybersecurity and privacy risks, providing a unified platform that aligns with the broader risk management strategy.
Balancing Multiple Risk Considerations: IRM provides a comprehensive view of all risk domains, ensuring alignment between cybersecurity risk management activities and other areas.
Enabling the Iterative Cycle of Risk Communication: IRM supports continuous risk communication, allowing for agile and informed decision-making.
Integrating Cybersecurity and ERM: IRM aligns cybersecurity risks with other organizational risks, providing a comprehensive view of the organization's risk landscape.
IRM's Role in Continuous Improvement: IRM technology ensures that all aspects of risk management are integrated into a unified strategy.
Facilitating Monitor-Evaluate-Adjust Cycle: IRM technology aligns cybersecurity risk activity with other types of risks, ensuring a cohesive approach.
Utilizing IRM for Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) and Key Risk Indicators (KRIs): IRM aligns metrics with the enterprise risk strategy, ensuring organizational alignment.
Source: IRM Navigator™ - Wheelhouse Advisors LLC
Bridging the Gaps: How IRM Links Risk Management Disciplines
IRM technology serves as the linchpin that integrates various risk management disciplines:
Information Technology Risk Management (ITRM): IRM ensures that technology risks, including cybersecurity risks, are aligned with broader business objectives. It integrates IT-related risks with the overall risk management strategy, recognizing that cybersecurity risks are inherent in technology management.
Operational Risk Management (ORM): IRM ensures that operational risks, including cybersecurity risks, are integrated with the broader risk management goals of the organization. It recognizes that cybersecurity risks can impact day-to-day operations and must be managed in conjunction with other operational risks.
Governance, Risk, and Compliance (GRC): IRM integrates GRC with the broader risk management framework, recognizing that cybersecurity risks can impact compliance and governance. It ensures that organizations are not just compliant but are also effectively managing the risks associated with non-compliance, including cybersecurity risks.
Enterprise Risk Management (ERM): At the heart of IRM is ERM, which provides a comprehensive view of all risks across the organization. IRM ensures that ERM principles are integrated with cybersecurity risk management, aligning all risks, including cybersecurity, with the broader organizational strategy.
The Comprehensive Approach to Cybersecurity with IRM
IRM technology not only bridges the gaps between various risk disciplines but also provides a comprehensive approach to cybersecurity. Here's how:
Unified Risk View: IRM provides a single, unified view of all risks across the organization, including cybersecurity risks. This comprehensive view enables organizations to understand how different risks interrelate and impact each other.
Strategic Alignment: By aligning cybersecurity risks with overall business objectives, IRM ensures that cybersecurity efforts are not just about security but are also strategically aligned with the organization's goals and objectives.
Agile Risk Management: IRM enables organizations to be agile in managing risks, allowing them to quickly respond to changes in the risk landscape. This agility is particularly important in the fast-paced world of cybersecurity, where threats and vulnerabilities can change rapidly.
Comprehensive Risk Reporting: IRM provides comprehensive reporting capabilities, allowing organizations to understand their risk profile and make informed decisions. This reporting includes not just cybersecurity risks but all risks across the organization.
Integration with Existing Systems: IRM technology can integrate with existing systems and processes, ensuring that it fits seamlessly into the organization's existing risk management efforts.
Conclusion
The NIST CSF 2.0 and IRM technology represent a new era in cybersecurity. By bridging the gaps between ITRM, ORM, GRC, and ERM, IRM ensures that cybersecurity risks are fully integrated with the broader risk management strategy of the organization. This integration enables a more comprehensive approach to risk management, positioning organizations to navigate the complex landscape of modern cybersecurity.
For organizations looking to align with the NIST CSF 2.0, IRM technology offers a pathway to success, ensuring that risk integration is not just a goal but a reality.
For a deeper exploration of how Integrated Risk Management can revolutionize your organization's approach to risk, visit Wheelhouse Advisors.