
The RTJ Bridge is the new premium version of The RiskTech Journal, delivering fast-moving, strategically relevant insights for risk leaders navigating today’s digital business landscape.
Designed as the link between editorial commentary and in-depth research, The RTJ Bridge offers exclusive access to:
High-frequency insight notes on market shifts, regulatory signals, and emerging technologies
Executive briefings and editorial series including “The Risk Ignored”
Strategic previews of IRM Navigator™ research, including upcoming Risk Landscape Reports
Whether you're monitoring vendor moves, tracking governance shifts, or preparing for regulatory disruption, The RTJ Bridge equips you with actionable foresight.
The RTJ Bridge - The Premium Version of The RiskTech Journal
Subscribe to get access now
The RTJ Bridge Subscription is a premier resource for executives and professionals focused on the intersection of risk management and technology. It provides subscribers with access to a curated collection of articles and expert insights designed to enhance risk management strategies through technological innovation. With its online format, The RTJ Bridge offers flexible access to critical information, helping leaders make informed decisions and stay competitive.

Why ROI Calculators Miss the Mark on IRM
Integrated risk management (IRM) is routinely forced into an ROI framing that does not fit its economic reality. ROI implies attributable incremental cash flows. Integrated risk management more often delivers dividends, meaning distributed benefits that improve enterprise outcomes without consolidating into a single return stream. This matters because many ROI calculators in market are not integrated risk management native.
The ROI calculators are commonly legacy GRC instruments, siloed by compliance use case, optimized for cost-of-compliance narratives, and weak at quantifying cross-domain integration value, loss mitigation value, and AI trust constraints. Public positioning reinforces this bias through language that centers measurement around the GRC program rather than enterprise-wide outcomes. AI amplifies the gap. As AI moves from feature to operating model, the trust dividend becomes a gating factor for scale. Standards and regulatory regimes increasingly emphasize trustworthiness, transparency, accountability, and information obligations.

IRM50 OnWatch - One Year After Evolv, the Archer TRM Transition Is Still Playing Out
One year after Archer launched Archer Evolv as a next-generation, AI-powered SaaS offering, the most important signal for Technology Risk Management buyers is not the pace of feature announcements. It is the shape of the transformation Archer appears to be executing, and what that shape implies about where the TRM platform market is headed.

IRM50 OnWatch - Wolters Kluwer Acquires StandardFusion and Signals Audit Plus GRC Convergence Trend
Wolters Kluwer Corporate Performance & ESG (CP and ESG) signed and completed the acquisition of StandardFusion on January 9, 2026 for approximately €32 million in cash. StandardFusion is a Vancouver-based provider of cloud GRC software, and Wolters Kluwer states it will be integrated into TeamMate to create a more unified audit plus GRC offering.

IRM50 OnWatch - Diligent Acquires 3rdRisk, Signaling a Faster IRM Convergence of GRC and AI-Native Third-Party Risk
On January 14, 2026, Diligent announced its acquisition of 3rdRisk, a Netherlands-based, AI-native third-party risk management (TPRM) platform. Diligent positioned the deal as an expansion of its Diligent One Platform toward “AI-native third-party risk management at scale,” emphasizing automated vendor profiling, assessment workflows, and AI-driven document analysis to compress audit readiness timelines.
This transaction is not simply module expansion. It is a strategic signal that TPRM has moved from being a compliance-adjacent workflow into a board-visible risk domain that must operate continuously, particularly as regulatory expectations for supply chain and digital dependency oversight intensify.
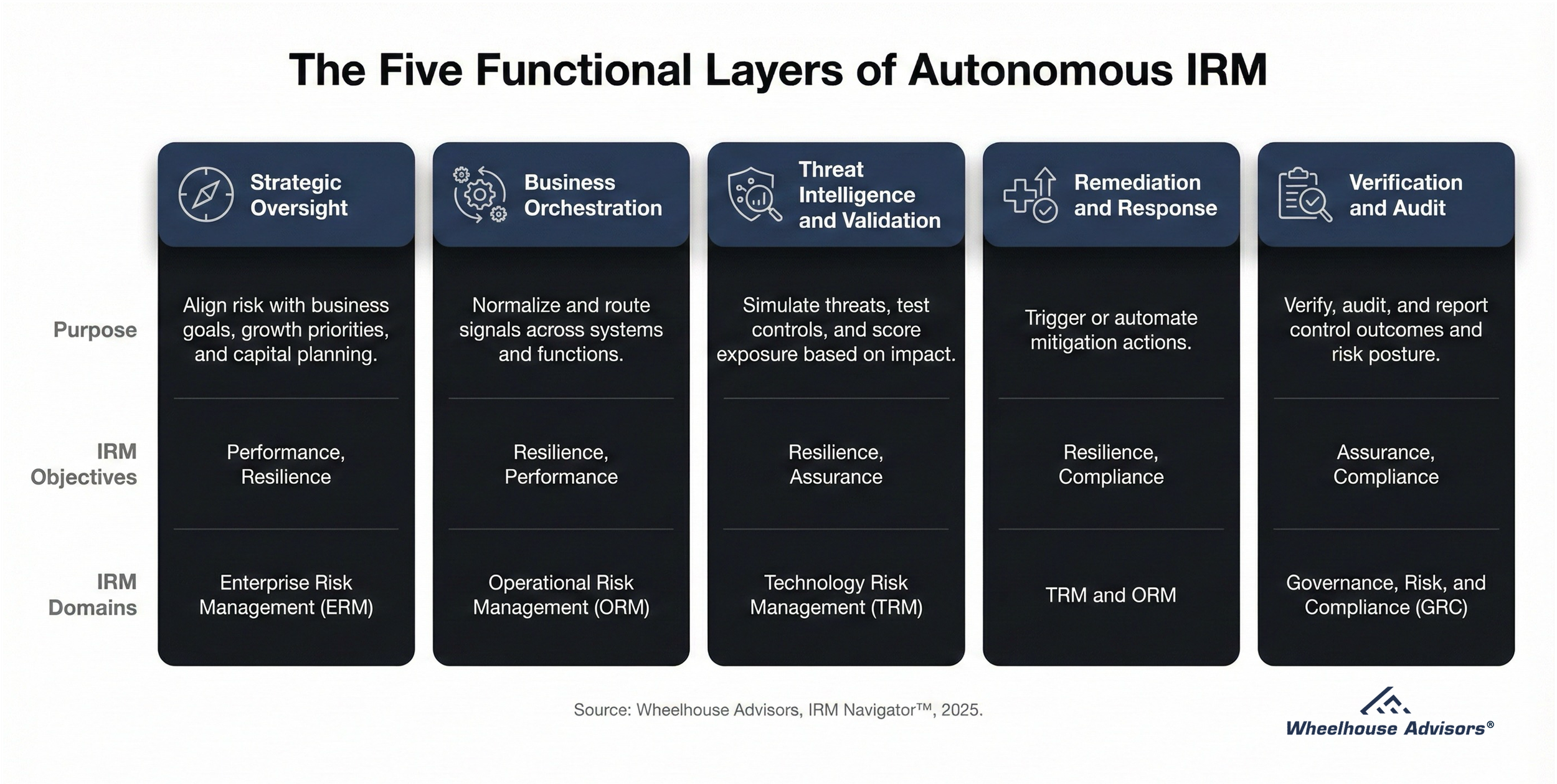
What NVIDIA’s CES 2026 Post Signals for Autonomous IRM
NVIDIA’s January 5, 2026, CES post is not “just a chip announcement.” It is a blueprint for making agentic systems cheaper to run, faster to execute, more distributed (from data center racks to desktops and edge), and more simulation-driven. For Autonomous Integrated Risk Management (Autonomous IRM), the practical implication is that the limiting factor shifts. It becomes less about whether the enterprise can afford the compute and more about whether it can manage autonomous decision loops with bounded execution, reliable orchestration, and audit-grade evidence.
What changed (and why executives should care)
Cadence shifts: more risk work can run continuously rather than quarterly because inference economics and long-context performance are improving.
Scope expands: autonomy moves beyond cyber and compliance into operational resilience and “physical” validation patterns that rely on simulation and long-tail testing.
Expectations rise: decision provenance and replayable evidence become baseline requirements, not premium features.
What follows is the translation of NVIDIA’s CES announcements into Autonomous IRM implications, using an executive pattern: signal, why it matters, implication, program design change, and a measurable buyer proof point.
IRM50 OnWatch - What the ServiceNow Armis Deal Signals for IRM
ServiceNow’s announced agreement to acquire Armis for $7.75 billion in an all-cash transaction (expected to close in the second half of 2026) is not just a cybersecurity expansion move. It is a market signal that “risk management at scale” is shifting toward a unified operating model where (1) real-time technology and asset intelligence, (2) prioritization logic, and (3) remediation and verification workflows increasingly sit on the same platform spine.
For IRM leaders, this matters because it tightens the linkage between technology risk signals and enterprise risk action, and it changes what “continuous monitoring” should mean in buyer evaluations.

What the EU’s Updated Sustainability Rules Mean for U.S. Companies
The European Union has reached a provisional political agreement to revise its sustainability reporting and supply-chain due-diligence framework. The agreement, completed under the Omnibus I package, significantly narrows the scope of both the Corporate Sustainability Reporting Directive (CSRD) and the Corporate Sustainability Due Diligence Directive (CSDDD). The revised thresholds remove obligations for many companies, particularly those headquartered outside the EU with smaller regional footprints.
However, the strategic direction remains unchanged. Large U.S. multinationals with material operations, revenue, or supply-chain exposure in the EU will continue to face substantial reporting, due-diligence, and legal liability requirements. The EU is signaling a long-term expectation that sustainability, human rights, and environmental risk management form an integrated component of corporate governance and enterprise risk programs.
For U.S. companies, the reduced scope is not an exemption from responsibility. It is an opportunity to mature risk capabilities, unify global sustainability reporting, and strengthen supply-chain due diligence before enforcement and investor scrutiny intensify.

Does GRC Need Finishing School? The IRM Navigator™ View on Forrester’s GRC ‘Grad School’ Story
Forrester's recent blog “GRC Platforms Enter Their Grad School Era” contains a notable admission. The analysts describe GRC as "old enough to be in grad school," yet still struggling to prove it can act as the workhorse technology for modern risk professionals. After roughly 20 years of formal coverage, the firm suggests that GRC is not yet fully ready for the “real world” of risk and now needs a kind of graduate-level evolution, built on continuous controls monitoring, quantification, and AI. This observation raises an obvious question. Does GRC really need finishing school after decades of market evolution, or have we been asking the category to do the wrong job?
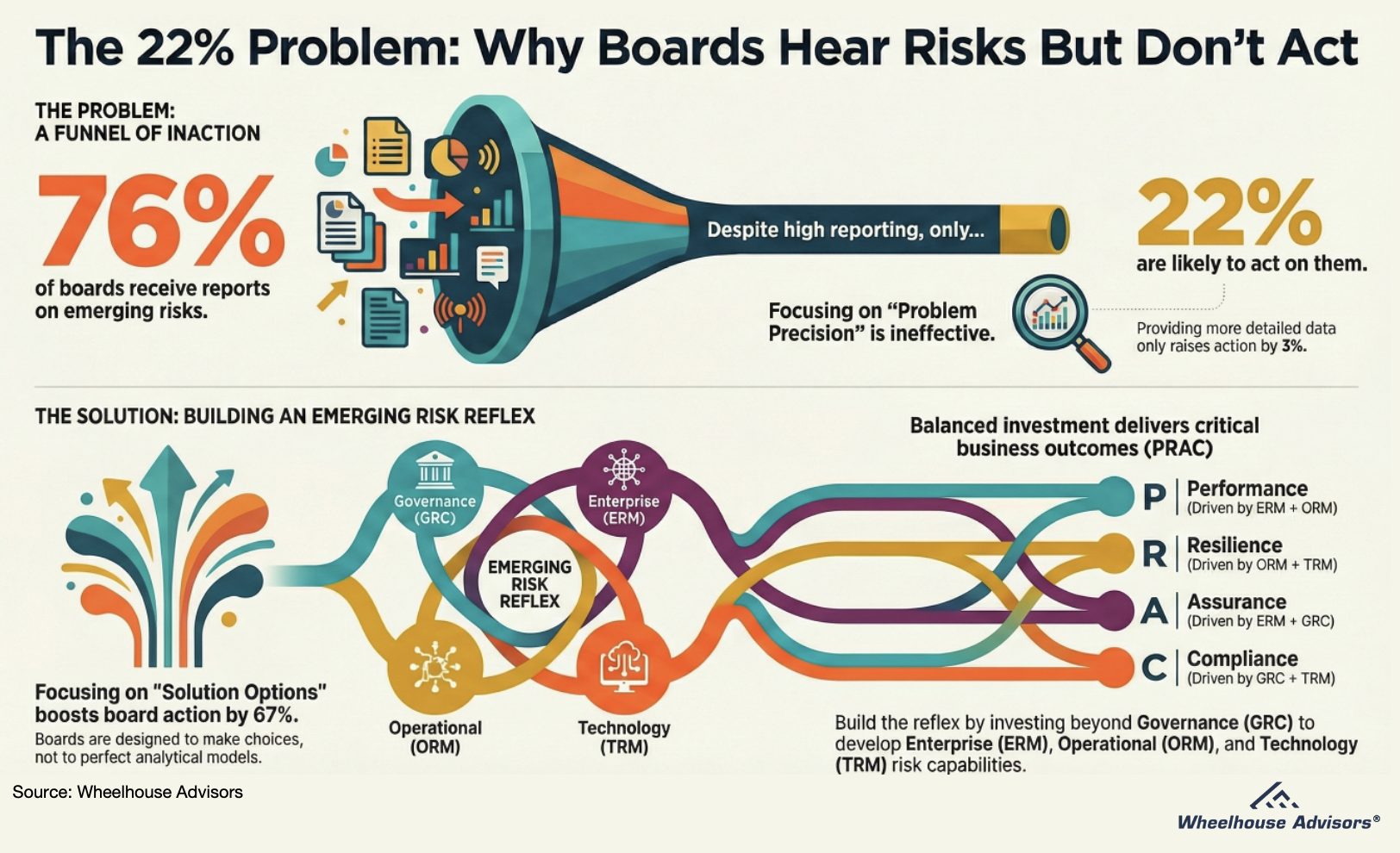
The 22 Percent Problem: Why Boards Hear the Risks but Still Do Nothing
If your board is hearing more emerging risks than ever and still doing almost nothing, you are not alone. Gartner data shows seventy-six percent of boards receive emerging risk reports, but only twenty-two percent are likely to act on what they hear. This IRM Navigator™ research note explains why that gap exists and how GRC-centric investment quietly builds oversight while starving your organization of reflex. If you are tired of “noted” being the only outcome, this is the playbook for turning emerging risk insight into action.

The Static Quadrant: Why GRC Stopped Moving
The “2025 Gartner® Magic Quadrant™ for Governance, Risk and Compliance (GRC) Tools, Assurance Leaders” offers more than an update on vendor positioning. It captures a defining moment in the evolution of enterprise risk management technology. For the first time since Gartner began coverage of this market in 2008, the Visionaries quadrant is completely empty.
This absence is not an error or a symptom of decline. It is a reflection of structural maturity and the point at which a technology category stops expanding outward and begins to integrate inward. The GRC segment has stabilized around its purpose: to deliver reliable assurance, compliance automation, and control verification at scale.
This research note is a follow-up to the recent RiskTech Journal article, GRC Without Visionaries: What the 2025 Gartner® Magic Quadrant™ Reveals About the Future of Risk. It further examines why the quadrant has gone static, why that matters, and how the integration of GRC within the broader Integrated Risk Management (IRM) model marks a necessary and healthy progression. It concludes that the current stillness in GRC represents not the end of innovation, but the beginning of Assurance Intelligence. It is the fusion of compliance evidence, operational data, and AI-enabled assurance that will define risk management by 2032.

Agentic AI Moves From Hype to Operating Model: What Risk Leaders Must Do Now
EY’s newest global insight, “What Risk Leaders Need to Do Now About Agentic AI,” sets a clear challenge: organizations that treat agentic AI as another productivity initiative risk amplifying exposure, not mitigating it. The report argues that risk functions must now move beyond experimentation and build an enterprise operating model where autonomous and semi-autonomous agents can act safely, transparently, and in alignment with strategy.
This message reinforces a structural shift already underway in Integrated Risk Management (IRM). Wheelhouse Advisors’ Autonomous IRM model defines how these agentic systems should operate—not as isolated bots or chat interfaces, but as integrated decision engines that connect strategic intent, operational execution, and assurance validation.

Workiva’s Q3 2025 Results Signal the Rise of “Assured Data Platforms” in the IRM Market
Workiva’s Q3 2025 results represent more than a financial beat—they reveal a strategic inflection point for the Integrated Risk Management (IRM) market. The company delivered total revenue of $224 million, up 21% year over year, with subscription and support revenue growing 23%. Its non-GAAP operating margin expanded to 12.7%, nearly tripling from the prior year. Just as significant, customers with annual contract value (ACV) above $500,000 rose 42%, confirming enterprise-scale adoption of Workiva’s unified disclosure and assurance platform.
This growth underscores a broader market movement toward “assured data platforms”—solutions that unify financial, sustainability, and risk reporting within one governed architecture. As ESG regulation, audit digitization, and AI assurance converge, Workiva’s performance signals what IRM leaders should expect across the next phase of market maturity.

ServiceNow Q3 2025 Through an IRM Market Lens
ServiceNow’s Q3 2025 performance is a clear demand signal for platform-centric Integrated Risk Management. The company reported subscription revenue of 3.299 billion dollars, up 21.5 percent year over year, with strong large-deal activity and a raised full-year subscription outlook. These results, combined with the AI Control Tower launch and continued Now Assist upgrades, indicate that buyers are consolidating GRC, technology risk, and assurance workflows on a single operating platform that can also govern AI models, agents, and evidence. This is an accelerant for IRM programs that seek unified taxonomies, end-to-end traceability, and continuous control monitoring across ERM, ORM, TRM, and compliance functions.

Reinventing Risk Management Through Integrated Risk, A PwC and OneTrust Perspective
PwC and OneTrust have published a concise eBook that advocates for a unified, digital operating model for risk, and positions their alliance to deliver it. The document highlights pressure on risk and compliance teams, presents recent PwC survey signals on funding and prioritization gaps, and outlines an “IRM ecosystem mindset” anchored in OneTrust’s modular platform and PwC’s implementation services.

IRM50 OnWatch: Acquisitions and Partnerships Signal Further Movement Away from Stand-alone GRC to Unified IRM
This past week, the IRM market took a decisive step toward operationalizing AI oversight at scale. AuditBoard moved first with a definitive agreement to acquire FairNow, a purpose-built AI governance platform, and expanded its alliance with EY US to pair platform capabilities with consulting delivery. In parallel, boardroom and sustainability workflows tightened through a new Diligent–Persefoni partnership, and specialized compliance players announced alliances that round out the IRM ecosystem. The signal is clear: buyer demand is shifting from point capabilities to unified operating models that align platforms, data, and services across Performance, Resilience, Assurance, and Compliance.

Agentic Operational Risk: How AI Is Reshaping Control, Performance, and Resilience
Operational risk management is evolving from reactive oversight to intelligent orchestration. Agentic AI, systems that can plan, tool, and act with bounded autonomy, is at the center of this shift. These agents compress cycle times, expand control coverage, and deliver evidence with audit grade traceability. Within the IRM Navigator™ Model, they strengthen the connection between Performance and Resilience, the two objectives where ORM delivers the most tangible value.
EY’s Boomi Alliance Accelerates IRM+ into the Autonomous IRM Era
EY’s new alliance makes Boomi the preferred way to connect the many systems IRM+ depends on, move and manage the data they generate, and orchestrate AI (including AI agents) around IRM+ workflows. IRM+ itself continues to be anchored on ServiceNow for risk workflows; Boomi primarily strengthens the integration, data, and AI layers around it.

Bridging the Divide: How ServiceNow’s AI Experience Could Unify TRM and IRM
ServiceNow’s latest innovation, AI Experience, introduces a unified conversational interface that could redefine how organizations manage risk. Far from being another “AI assistant,” this platform-level integration embeds natural language and multimodal intelligence across workflows, connecting Technology Risk Management (TRM) with Integrated Risk Management (IRM) in ways that make risk management feel less like a process and more like a conversation. This commentary explores how AI Experience extends ServiceNow’s TRM and IRM capabilities, why it represents a major shift toward unified risk intelligence, and how it aligns with the Performance, Resilience, Assurance, and Compliance (PRAC) objectives of the IRM Navigator™ Model.

Aon GRMS Survey 2025: Integrated Risk Management Moves From Slogan to System
Aon’s 2025 Global Risk Management Survey frames the environment as a system of overlapping risks that cannot be managed effectively in silos. The “Top 10 Global Risks” chapter states that organizations that adopt a proactive, integrated approach can turn complexity into opportunity. This aligns directly with the IRM Navigator™Model and its PRAC objectives, Performance, Resilience, Assurance, and Compliance, operated as one cadence rather than separate projects.

The Exponential Ripple: How JLR’s Cyber Incident Exposed the Interconnected Matrix of Risk, and How PRAC Stops the Spread
A month after Jaguar Land Rover’s cyber incident, the story is no longer only about one company’s outage. It is about the exponential ripple that travels through a tightly coupled production and supplier network, then into finance, regulation, and public policy. The United Kingdom moved to stabilize the sector with a £1.5 billion loan guarantee through UK Export Finance, a partial backstop intended to unlock working capital from commercial banks and push liquidity down the supply chain. Reporting also confirms that JLR had no cyber insurance at the time of the attack, and that recovery will take months rather than days, with additional bank facilities arranged alongside the guarantee.

